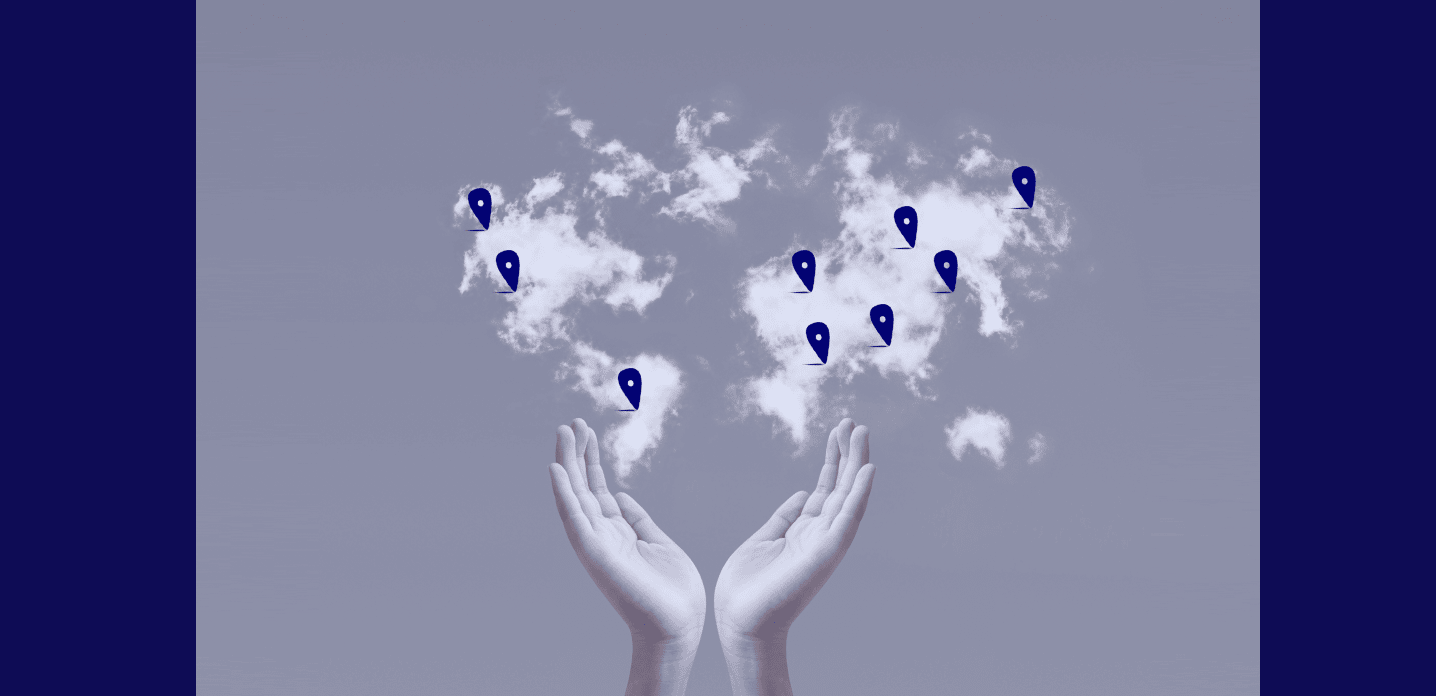
Some people believe that because data is easily accessible through the cloud the location of data centers doesn’t really matter. However, for many applications the opposite is true: the physical location of the computer servers plays a crucial role in its overall performance.
Why? Data locality improves system throughput. Moving gigabytes of data between systems and nodes consumes massive bandwidth and slows down other operations. Data locality solves this issue by moving computation to the data rather than moving the data to computation.
In other words, cloud services that are close to the local users reduce network latency caused by long connections.
A Distributed System: The Advantages
According to Gartner, distributed computing systems are becoming a primary service that all cloud services providers offer to their clients. Why? Because the advantages of distributed cloud computing are extraordinary.
Distributed systems and cloud computing are a perfect match that powers efficient networks and makes them fault-tolerant. Let’s examine some of the basics of distributed systems:
1. Collaboration
A distributed computing system is a collection of multiple physically separated servers and data storage that reside in different systems worldwide. These components collaborate to achieve the same objective, giving an illusion of being a single, unified system with powerful computing capabilities.
2.Choice of Location
As resources are globally present, businesses can select cloud-based servers near end-users and speed up request processing. Companies reap the benefit of edge computing’s low latency with the convenience of a unified public cloud.
3.Processing & Performance
Distributed clouds allow multiple machines to work on the same process, improving the performance of such systems by a factor of two or more. As a result of this load balancing, processing speed and cost-effectiveness of operations can improve with distributed systems.
4. Independent Systems
All nodes of the distributed network are independent computers. You can easily add or remove systems from the network without resource straining. Scaling with distributed computing services providers is easy. Automated processes and APIs to help them perform better.
5. Compliance
Distributed cloud infrastructure helps businesses use local or country-based resources in different geographies. This way, they can easily comply with varying data privacy rules, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California.
Ridge’s Distributed Cloud: Solving the Location Problem
A data center model has been developed by Ridge in which existing data center infrastructure is federated into a unified network. Application owners can choose to deploy their services in any of these locations.
Ridge doesn’t own any of these data centers, but partners with their owners to provide cloud services. Each partner owns one or more cloud offerings that supply resources to Ridge customers as part of Ridge’s global ecosystem.
Although every data center has its own customized technology stack, the Ridge distributed ecosystem rapidly turns any partner into a Point of Presence (PoP) in Ridge’s cloud.
When working on Ridge, the developer is agnostic to the specific stack technology of each data center. He or she needs only to interact with a single API in order to deploy applications locally and to leverage Ridge cloud-native services, such as managed Kubernetes, containers, and object storage.
As an alternative to the traditional public cloud model, Ridge enables application owners to utilize a global network of service providers instead of relying on the availability of computing resources in a specific location. Enterprises are empowered to deploy in any location they need to be in.
Read more about this topic in another of our blogs: What is Distributed Computing.